In the ever-evolving landscape of cryptocurrency, one strategy has gained significant traction among investors seeking higher returns-yield farming. This innovative investment approach has reshaped the way individuals interact with decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, presenting opportunities to generate substantial profits. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamentals of yield farming, from its core concept to the associated risks and rewards.
What is Yield farming?

Yield farming is a high-risk, high-reward investment strategy that involves lending or staking cryptocurrency assets in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to earn interest or rewards. DeFi protocols are peer-to-peer financial applications that run on blockchain technology and allow users to interact with financial services without the need for intermediaries like banks or brokers.
To yield a farm, users typically deposit their crypto assets into liquidity pools or lending protocols. Liquidity pools are used to power decentralized exchanges (DEXs), while lending protocols allow users to borrow and lend crypto assets. In return for providing liquidity or lending their assets, yield farmers are rewarded with interest or tokens.
The amount of interest or rewards that yield farmers earn can vary depending on the protocol, the crypto assets they deposit, and the current market conditions. However, yield farming can be a very lucrative way to generate passive income.
What is a Yield Farmer?
A yield farmer is a cryptocurrency investor who uses decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to generate passive income. Yield farmers typically stake or lend their crypto assets to liquidity pools or other DeFi protocols in exchange for interest or rewards.
Yield farming is a relatively new investment strategy, but it has quickly become one of the most popular ways to earn passive income in the crypto space. This is because it can generate very high returns, especially for early adopters of new projects. It is important to note that yield farming is also a very high-risk investment strategy.
How does Yield farming work?

Yield farming works by providing liquidity to DeFi protocols. When users stake or lend their crypto assets to a DeFi protocol, they are essentially providing liquidity to that protocol. This liquidity allows other users to trade, borrow, and lend crypto assets on the protocol. In return for providing liquidity, yield farmers are rewarded with interest or rewards.
Here is a simple example of how yield farming works:
- A user deposits 10 ETH and 10 BTC into a liquidity pool on a DEX.
- The liquidity pool is used by traders to swap ETH and BTC.
- In return for providing liquidity, the user earns interest on the fees generated by the pool.
- The user can also earn rewards in the form of tokens from the DEX.
- The amount of interest and rewards that the user earns will depend on a number of factors, such as the trading volume on the DEX and the current price of ETH and BTC.
What is APY in Yield Farming?
APY, or annual percentage yield, is a measure of the return on investment (ROI) for a yield farming strategy. APY takes into account the compounding effect of interest, which means that the actual ROI can be higher than the stated APY.
In yield farming, APY is typically used to measure the returns on liquidity mining and lending strategies. For liquidity mining, APY is calculated based on the amount of interest and trading fees that liquidity providers earn. For lending, APY is calculated based on the amount of interest that lenders earn.
APY can vary widely depending on the DeFi protocol, the crypto assets deposited, and the current market conditions. However, APY can be a very useful metric for comparing different yield farming strategies.
Types of Yield Farming
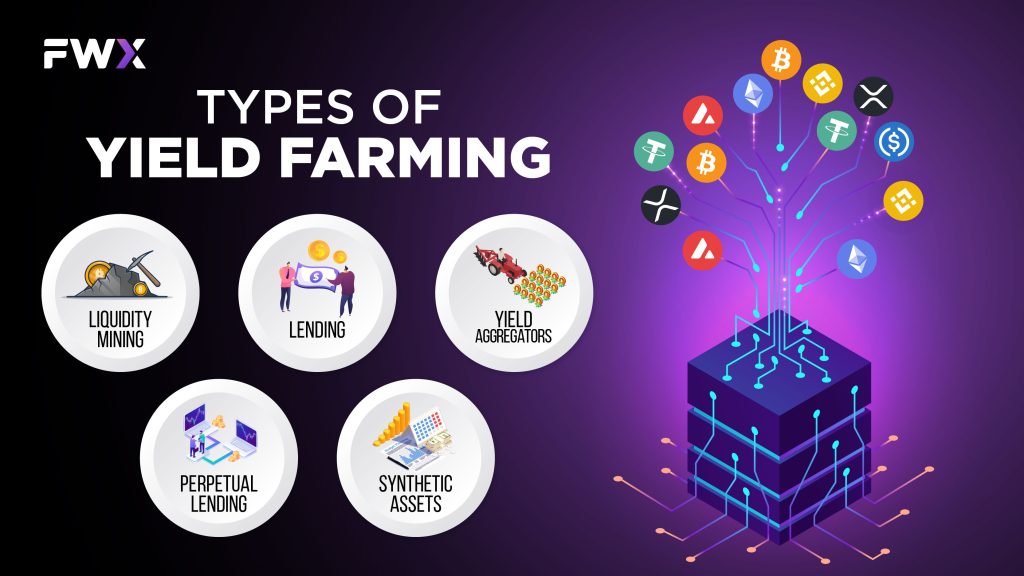
- Liquidity mining: Liquidity mining involves depositing crypto assets into liquidity pools. Liquidity pools are essential for the operation of decentralized exchanges (DEXs), as they allow users to trade crypto assets without the need for an intermediary. In return for providing liquidity, liquidity miners are rewarded with interest and trading fees.
- Lending: Lending involves depositing crypto assets into a lending protocol. Lending protocols allow users to borrow and lend crypto assets. In return for lending their assets, lenders are rewarded with interest.
In addition to these two main types, there are also a number of other yield farming strategies that have emerged in recent years. These include:
- Yield aggregators: Yield aggregators are platforms that automatically invest user funds across a variety of different yield farming protocols. This can help users to maximize their returns while minimizing their risk.
- Perpetual lending: Perpetual lending is a type of lending where there is no fixed repayment date. This type of lending can be used to generate higher returns, but it also comes with a higher risk.
- Synthetic assets: Synthetic assets are digital assets that track the price of another asset, such as a stock or commodity. Yield farmers can use synthetic assets to generate exposure to different asset classes without having to purchase the underlying assets themselves.
Benefits of Yield Farming
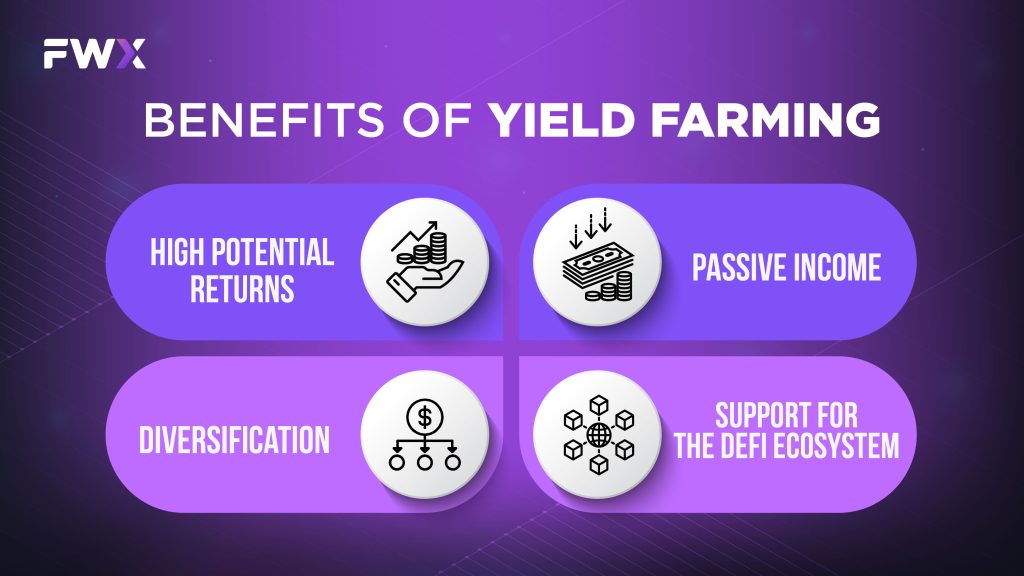
- High potential returns: Yield farming can generate very high returns, especially for early adopters of new projects.
- Passive income: It is a relatively passive way to generate income. Once you have deposited your crypto assets into a liquidity pool or lending protocol, you can earn interest or rewards without having to do anything else.
- Diversification: It can be a good way to diversify your crypto portfolio. By staking or lending different crypto assets, you can reduce your risk exposure.
- Support for the DeFi ecosystem: Yield farming helps to support the DeFi ecosystem by providing liquidity to DEXs and lending protocols. This makes it easier for users to trade and borrow crypto assets.
Risks of Yield Farming

Yield farming is a high-risk investment strategy, and there are a number of things that can go wrong. Some of the most common risks include:
- Smart contract risk: DeFi protocols rely on smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts that run on blockchain technology. If there is a bug in a smart contract, it could be exploited by hackers and result in the loss of funds.
- Volatility: The crypto market is notoriously volatile. This means that the value of your crypto assets can fluctuate wildly, which could result in losses.
- Impermanent loss: Impermanent loss is a risk associated with liquidity mining. It occurs when the price of the crypto assets in a liquidity pool changes significantly.
- Rug pulls: Rug pulls are a type of fraud where the developers of a DeFi protocol abandon the project and take all of the user funds with them.
Other risks include:
- Technical risks: Yield farming can be complex and technical, and there is a risk of making mistakes.
- Administrative risks: Yield farmers may need to pay fees, such as gas fees or liquidity pool fees.
- Regulatory risks: The regulatory landscape for DeFi is still evolving, and there is a risk that new regulations could be introduced that could have a negative impact on yield farming.
Conclusion
Yield farming is a high-risk, high-reward investment strategy that involves lending or staking cryptocurrency assets in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to earn interest or rewards. DeFi protocols are peer-to-peer financial applications that run on blockchain technology and allow users to interact with financial services without the need for intermediaries like banks or brokers.
Yield farming can be a very lucrative way to generate passive income, but it is important to understand the risks involved before investing.


