The use of blockchain-based technologies has become prevalent in various applications that are closely related to our daily lives. These include cryptocurrencies, tokenomics, business applications, Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications, and more. One such application that is growing rapidly and attracting significant attention from academia and governments worldwide is the Decentralized Autonomous Organization. While DAO has presented many opportunities for blockchain technologies, it is surprising to note that there is a lack of an overview of DAO from the perspective of blockchains.
What is a DAO?

DAO is a type of organization that operates using a software program based on blockchain technology. This allows for decision-making and management to be decentralized. The program executes the organization’s rules and regulations automatically without the need for human intervention.
Unlike traditional organizations, which have a centralized authority that manages its operations and makes decisions, DAOs are fully decentralized. This means that decisions are made through a voting system based on consensus among its members. The rules and regulations of the DAO are encoded in the software, which operates autonomously.
DAOs have the potential to change the way organizations operate by eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks and legal entities. This results in a more direct, transparent, and democratic decision-making process. DAOs can be used for various activities such as managing investments, running decentralized applications, and creating new cryptocurrency projects.
However, DAOs are not without risks. They may be vulnerable to hacking, and there is a potential for malicious actors to manipulate the voting process. It’s crucial to note that the legal and regulatory status of DAOs is still developing, and there may be legal and compliance risks involved in using them.
How do DAOs work?

DAOs operate as a decentralized entity without the need for a central authority or intermediaries. They use blockchain technology to accomplish this. A DAO is typically composed of individuals with a shared goal or interest. The rules and regulations are encoded into a smart contract on a blockchain network like Ethereum. Once the smart contract is deployed, the DAO becomes a self-governing entity that operates automatically.
DAO members interact with the smart contract by using tokens that represent their ownership stake in the organization. The decision-making process is carried out using a consensus-based voting system, where members can vote on proposals using their tokens, and the smart contract executes the decision.
The activities and operations depend on its purpose and goals. Some DAOs are involved in managing investments, while others focus on supporting decentralized applications. DAOs offer a more democratic and transparent decision-making process than traditional organizations and are often more efficient and cost-effective because they don’t require intermediaries.
How to launch a DAO project?

The launch of a DAO project goes through a sequence of steps, which are as follows:
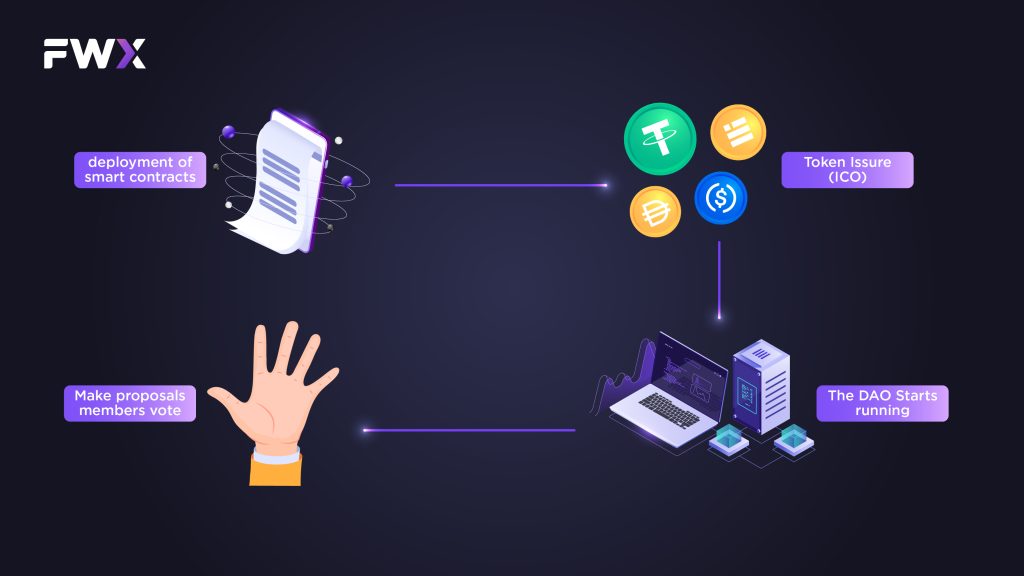
- Developing and deploying smart contracts based on predefined rules.
- Managing the token issuance through ICOs during the initial funding stage.
- Starting the DAO operations once the funding phase is over.
- Presenting proposals, followed by voting by members on the proposals.
After the initial launch of a DAO, there are several concerns that are important for its ongoing success and growth:
- Building a community: A DAO is only as strong as its community. Building and maintaining an engaged and active community is critical for the success of a DAO.
- Establishing governance and decision-making processes: A DAO must have clear and transparent governance structures, as well as decision-making processes that allow members to participate in the decision-making process.
- Developing a roadmap: A DAO must have a clear roadmap that outlines its goals and objectives. The roadmap should be regularly updated to ensure that the DAO stays on track and remains relevant.
- Monitoring and updating: It’s important to monitor the DAO’s smart contracts and governance structure to ensure that they are working as intended. Updates should be made as necessary to improve the DAO’s performance and security.
- Compliance: A DAO must comply with legal and regulatory requirements. This includes ensuring that it is transparent about its activities and complying with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations.
Problems and solutions of blockchains
The hacking incident that occurred with the first The DAO project prompted a reflection on the project. The first generation of blockchain technology, known as Blockchain 1.0, was primarily created for cryptocurrency purposes. The second generation, Blockchain 2.0, represented by Ethereum, is an open platform that enables a new decentralized computing paradigm. The DAO operates on the Ethereum platform. While there are no apparent security vulnerabilities in pure cryptocurrency systems like Bitcoin, the second-generation blockchain applications and semantics can introduce security vulnerabilities. Additionally, from a social development perspective, some researchers have identified common problems that need to be addressed in both blockchains and the DAO.
The typical issues that require attention include the interpretation of fork culture following the hacker event, potential problems in the development of distributed ledger technology (DLT) applications, and the question of whether the main trend of blockchain technology is reasonable. These questions have sparked discussions about blockchain system hacker attacks, security issues, and counter-trend issues within the blockchain community. The solutions are as follows:
- security threats and enhancement solutions in blockchain,
- scalability of blockchain,
- countervailing trend,
- future of the DLT.
How does a DAO make money?

- Investment management: A DAO can manage investments in various assets, such as cryptocurrencies, stocks, or real estate. The DAO earns money by investing in these assets and earning returns on its investments.
- Fees: A DAO can charge fees for its services, such as transaction fees for using its platform or membership fees for being part of the organization.
- Crowdfunding: A DAO can use crowdfunding to generate revenue for its projects. It may offer tokens in exchange for funding, and the value of these tokens can increase as the project progresses.
- Decentralized applications (DApps): A DAO can create DApps that generate revenue through various means, such as in-app purchases or advertising revenue.
- Governance tokens: A DAO can issue governance tokens that allow holders to participate in decision-making and vote on proposals. These tokens can increase in value as the DAO grows and becomes more successful.
- Staking: A DAO can earn money through staking, which involves holding and validating cryptocurrency transactions on a blockchain network. The DAO earns a percentage of the transaction fees for its staking services.
- Liquidity provision: A DAO can provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges, earning fees for its services.
- Data monetization: A DAO can monetize data generated by its operations or by its members, selling it to third-party companies or using it for targeted advertising.
Where can you invest in DAO?

- Aragon: Aragon is platform that allows users to create and manage decentralized organizations on the Ethereum blockchain.
- MolochDAO: MolochDAO is a community-driven DAO that funds Ethereum-based projects through a decentralized decision-making process.
- MakerDAO: MakerDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization that operates the Maker protocol, which allows users to generate and trade the DAI stablecoin.
- DAOstack: DAOstack is a framework for building decentralized autonomous organizations that provides tools for governance, decision-making, and collaboration.
- GnosisDAO: GnosisDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization that enables collective decision-making and resource allocation on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Colony: Colony is a platform for creating and managing decentralized organizations that enables users to collaborate, coordinate, and make decisions in a decentralized manner.
Conclusion
In summary, a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is a revolutionary blockchain-based concept that operates without a central authority. While offering transparency and efficiency, DAOs also face challenges like security and regulatory compliance. Their success depends on community building, governance, and revenue generation. Projects like Aragon, MolochDAO, MakerDAO, DAOstack, GnosisDAO, and Colony are pioneering DAO development. DAOs represent a dynamic frontier in blockchain technology, offering new possibilities for decentralized decision-making, but their potential must be balanced with careful consideration of risks and challenges.


