In this article, Forward will take you to know what is Blockchain, including real working examples of blockchain in various companies, for anyone who wants to know more about how this technology, which is the backbone of bitcoin currency, is going to change the world.
What is blockchain?

It is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. These transactions are grouped together in blocks and linked together chronologically, forming a chain of blocks, hence the name “blockchain.”
Each block contains a timestamp, a reference to the previous block, and transaction data. Because each block contains a reference to the previous one, the chain is able to link all the way back to the very first block, known as the genesis block.
One of the key features of this technology is that it is immutable, meaning that once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered. This ensures that the data stored on the blockchain is tamper-proof and cannot be corrupted or deleted.
It can be used for a wide range of applications, such as digital currencies, supply chain management, and voting systems. The most well-known application of this technology is the digital currency Bitcoin, which uses a blockchain to record and verify transactions on its network.
There are different types of these networks, including public and private blockchains. Public blockchains, such as Bitcoin, are open to anyone, and transactions are recorded in a transparent and decentralized way. Private blockchains, on the other hand, are permissioned and typically used for specific enterprise and business purposes.
This technology has the potential to revolutionize many industries by providing a secure and transparent way of recording and verifying transactions. However, there are also concerns about the energy consumption and scalability of networks.
What does a blockchain do?
This technology enables the creation of a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. This decentralized architecture allows for various use cases that are not possible with traditional centralized systems.
- Record Keeping: It can be used to record and track various types of data, including digital transactions, digital contracts, and other digital information. The data recorded on a blockchain is secure and tamper-proof, as each block in the chain contains a reference to the previous block, and once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered.
- Decentralization: It enables decentralization by allowing multiple parties to have access to and maintain a copy of the same ledger. This eliminates the need for a centralized authority, such as a bank, to oversee and validate transactions.
- Security: Decentralization and the use of cryptographic techniques like Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) make the data recorded secure and protected against tampering and other forms of malicious attacks.
- Transparency: Transactions recorded on a blockchain are visible to all parties on the network, providing transparency and accountability.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. This allows for the automatic execution of the contract, without the need for intermediaries, which makes transactions more efficient and cost-effective.
- Tokenization: It can be used for the tokenization of assets, turning physical assets like real estate or artwork into a token that could be traded on a platform.
- Supply Chain Management: It can be used to create a transparent and secure system for tracking the movement of goods and materials through the supply chain. This can help to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of fraud and other issues.
Overall, this technology has the potential to disrupt and revolutionize many industries by providing a secure and transparent way of recording and verifying transactions, allowing for more efficient and decentralized systems, and enabling new use cases, such as smart contracts and tokenization.
What is blockchain in simple terms?
terms and conditions refer to the legal agreements that govern the use of a blockchain-based service or product. These agreements typically outline the rights and responsibilities of the parties involved, including the user and the provider of the service or product.
Some common terms and conditions found in agreements include:
- Intellectual property rights: Who owns the rights to the technology and data on it. This can include the software code, patents, trademarks, and any other intellectual property associated with the service or product.
- Security and privacy: The measures taken to protect user data and transactions on it. This can include details on how data is stored, encrypted, and transmitted, as well as the measures taken to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Liability and indemnification: The responsibilities of the parties in the event of a security breach or other loss of data. This can include details on who is responsible for any losses, and the steps that will be taken to mitigate damages.
- Governing law and jurisdiction: The jurisdiction in which the agreement will be governed and any disputes will be resolved. This can be important in determining which laws will apply to the service or product, and where legal disputes will be heard.
- Token usage: The terms and conditions of using any tokens or cryptocurrency associated with the blockchain service or product. This can include details on how the tokens can be acquired, used, and traded, as well as any restrictions on their use.
- Compliance: The terms and conditions of compliance with laws, regulations, and standards that apply to the service or product. This can include details on how the service or product is compliant with laws and regulations related to money laundering, fraud, and other financial crimes.
- Dispute resolution: The terms and conditions of how disputes will be resolved, whether it’s through arbitration, mediation or court litigation.
- Force majeure: The terms and conditions that outline the actions that the parties will take in the event of an unforeseeable circumstance that affects the performance of the agreement.
What are the types of blockchain networks?
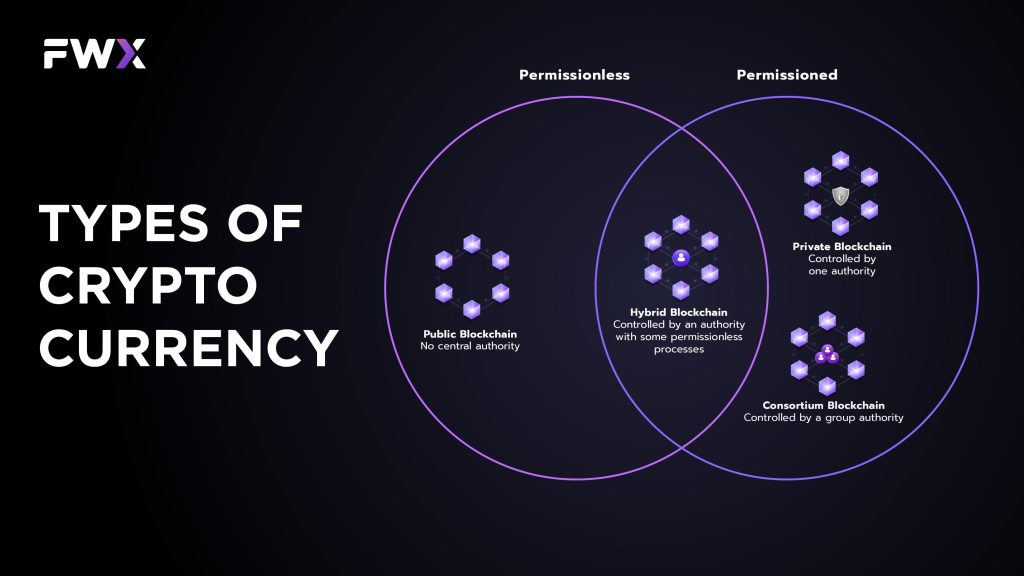
There are several types of blockchain networks, including:
- Public blockchain: A public blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger that is open to anyone who wants to participate. It allows anyone to join the network, validate transactions, and create new blocks. Examples of public blockchains include Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Private blockchain: A private blockchain is a centralized and permissioned ledger that is only accessible to a specific group of participants. It is typically used by businesses and organizations that want to keep their transactions and data private and secure. Examples of private blockchains include Hyperledger and Corda.
- Hybrid blockchain: A hybrid blockchain is a combination of both public and private blockchain characteristics. It allows for both public and private transactions to take place on the same network, providing the benefits of both types.
- Consortium blockchain: A consortium blockchain is a network of multiple organizations or companies that come together to create a decentralized and distributed ledger. It allows for a group of pre-selected and trusted participants to validate transactions and create new blocks, making it more secure and efficient than a public blockchain. Examples of consortium blockchains include R3’s Corda and the Ethereum Enterprise Alliance.
What is a blockchain example?

One of the most well-known examples of blockchain technology is the digital currency Bitcoin.
In the case of Bitcoin, the blockchain is used to record and verify transactions on its network. When someone wants to make a transaction, such as sending Bitcoin to another person, the transaction is broadcasted to the network.
Nodes, which are computers running Bitcoin software, then work to verify the transaction and ensure that the person making the transaction has enough Bitcoin to complete it. Once the transaction is verified, it is grouped with other verified transactions into a block.
This block is then added to the existing chain of blocks, creating a permanent and unchangeable record of all the transactions that have taken place on the Bitcoin network.
This system of recording and verifying transactions is decentralized, meaning that there is no central authority, such as a bank, overseeing the transactions. Instead, it is maintained by a network of users.
Another example:
- Supply Chain Management: Companies are using technology to create a transparent and secure system for tracking the movement of goods and materials through the supply chain. This helps to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of fraud and other issues.
- Voting systems: where each voter gets a unique token that they can use to cast their vote once. This ensures that the vote is not tampered with and prevents multiple voting by the same person. This can be very useful in countries where voting fraud is prevalent.
In summary, technology can be used in various industries and applications, like financial services, supply chain, voting and many others. Bitcoin is one of the well-known examples, but the possibilities for blockchain are numerous.
5 Example Companies Using Blockchain
- Walmart – The retail giant has been using technology since 2016 to track the movement of pork in China and later expanded the use to track the movement of other products such as lettuce and chicken in the United States. By using, Walmart is able to increase transparency and traceability in its supply chain, making it easier to track the movement of products from the farm to the store. This allows Walmart to quickly identify and address any issues that may arise, such as food safety concerns. In addition to increasing transparency and traceability, Walmart’s use of blockchain also helps to increase efficiency in its supply chain.
- Maersk – One of the world’s largest shipping companies, Maersk launched TradeLens, a blockchain-based platform for tracking the movement of shipping containers in 2017. By using, TradeLens is able to increase transparency and traceability in the shipping industry, making it easier for all parties involved in a shipment to track the movement of containers. This includes shippers, freight forwarders, customs authorities, and other parties. In addition to increasing transparency and traceability, TradeLens also helps increase shipping industry efficiency.
- IBM – IBM has been actively exploring and investing in it. They have developed a number of blockchain-based solutions for various industries, including supply chain management and finance. IBM’s blockchain platform, IBM Blockchain, allows businesses to build and host their own networks. IBM also offers a range of services such as consulting, development, and integration to help companies implement solutions.
- Provenance – Provenance is a UK-based blockchain start-up that is using blockchain technology to increase transparency and traceability in supply chains. They are working with companies in the food and fashion industries to build blockchain-based solutions for tracking the movement of products. By using it, Provenance helps companies to improve transparency and traceability in their supply chains, allowing them to quickly identify and address any issues that may arise, such as a food safety concern.
- Bitfury – Bitfury is a blockchain technology company that is using it to increase transparency and security in supply chain management. They have developed a blockchain-based platform called Exonum, which is being used by a number of companies in different industries to track the movement of goods. By using it, Exonum helps companies to improve transparency and traceability in their supply chains, allowing them to quickly identify and address any issues that may arise. The platform also includes features such as smart contract capabilities and data analytics, which helps companies to improve efficiency in their operations.
What is blockchain vs cryptocurrency?

Blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers. It is essentially a chain of blocks, each containing a number of transactions. Once a block is added to the blockchain, the data it contains cannot be altered, creating an immutable and tamper-proof record of all transactions that have occurred on the network. The decentralized nature of the blockchain means that it is not controlled by any single entity, making it resistant to censorship and fraud. The technology behind blockchain was first proposed in the early 1990s, but it wasn’t until the creation of Bitcoin in 2009 that the technology was used in practice.
Cryptocurrency, on the other hand, is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security and operates independently of a central bank. Bitcoin, the first and most widely-used cryptocurrency, was created in 2009 and it uses blockchain technology to record and verify transactions. Since then, thousands of different cryptocurrencies have been created, each with their own unique features and use cases. These digital currencies can be used to buy goods and services or traded like stocks on various online exchanges.
In summary, Blockchain is the underlying technology of cryptocurrency. It is a decentralized digital ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers, providing the foundation for the secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions that are the foundation of cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency is a digital currency that uses blockchain technology to operate, it is decentralized and operates independently of a central bank.


