Bitcoin, the world’s first and most prominent cryptocurrency, has experienced significant growth and adoption since its inception in 2009. One of the key aspects of Bitcoin’s design is a predetermined halving mechanism, which reduces the block reward for mining by 50% every 210,000 blocks, or approximately every four years. This event, known as a Bitcoin halving, plays a crucial role in regulating the supply of Bitcoin and influencing its price movements.
What is Bitcoin?

Bitcoin is a digital or virtual currency that uses peer-to-peer technology to operate without the need for a central authority. It is decentralized, meaning it is not subject to government or financial institution control. Bitcoin is often referred to as a cryptocurrency, which is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security.
Bitcoin was invented in 2008 by an anonymous person or group of people under the name Satoshi Nakamoto. The currency’s unit of account is the bitcoin (BTC), although there are also subdivisions of the bitcoin called millibitcoins (mBTC) and satoshis (sats). Bitcoins can be transferred between users via the Bitcoin network without the need for intermediaries.
Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain. Bitcoin is unique in that there is a finite number of them: 21 million.
Bitcoins can be used to purchase goods and services online and in some brick-and-mortar stores. They can also be traded on cryptocurrency exchanges for other currencies, such as US dollars or euros.
The value of Bitcoin is not backed by any physical asset, such as gold or silver, and it is subject to high volatility. However, Bitcoin has gained popularity due to its decentralized nature, potential for anonymity, and perceived limited supply.
What is Bitcoin Mining?

Bitcoin mining is the process of verifying and adding transaction records to the Bitcoin blockchain. Miners employ powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, and in return, they receive newly minted Bitcoins as a reward. This process is crucial for maintaining the integrity and security of the Bitcoin network.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
Transaction Verification: When a user makes a Bitcoin transaction, it broadcasts the transaction details to the entire Bitcoin network. Miners then collect these transactions and group them into a block.
Solving the Mathematical Problem: Miners use specialized hardware and software to solve a complex mathematical problem, known as a proof-of-work. The first miner to solve the problem successfully is rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins.
Adding the Block to the Blockchain: Once a miner solves the proof-of-work, they add the block containing the verified transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain. This process creates a permanent record of the transactions, ensuring their validity and preventing double-spending.
The Importance of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining plays a vital role in the Bitcoin network by:
Securing the Network: The proof-of-work algorithm makes it computationally expensive to tamper with the blockchain, protecting it from fraud and malicious attacks.
Validating Transactions: Miners verify the legitimacy of transactions, ensuring that all Bitcoin transactions are valid and recorded accurately.
Adding New Bitcoins to Circulation: The block reward for mining is the primary mechanism for introducing new Bitcoins into circulation.
What Is Bitcoin Halving?

Bitcoin halving is a predetermined event that occurs approximately every 210,000 blocks, roughly equivalent to every four years. During this event, the block reward for mining Bitcoins is reduced by half. This means that miners receive fewer Bitcoins for verifying transactions, effectively slowing down the pace of new Bitcoin issuance.
The halving process is embedded in the Bitcoin protocol and is automatically triggered after every 210,000 blocks. This predetermined schedule ensures a predictable and controlled reduction in the supply of new Bitcoins.
Why does bitcoin halve?
There are two primary reasons why Bitcoin halvings occur:
- To control the supply of Bitcoins: Bitcoin’s supply is capped at 21 million coins. This finite supply is one of the key characteristics that distinguishes Bitcoin from traditional fiat currencies, which can be printed at will by central banks. Halvings help to maintain Bitcoin’s scarcity by slowing down the rate at which new coins are created.
- To maintain the security of the Bitcoin network: Mining is the process of verifying and adding transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain. Miners earn newly minted Bitcoins as a reward for their work. Halvings help to ensure that mining remains profitable even as the supply of new coins decreases. This is important because miners play a crucial role in securing the network and preventing fraud.
Halvings have a significant impact on the Bitcoin ecosystem. They can affect the profitability of mining, the supply dynamics of Bitcoin, and overall market sentiment.
How does Bitcoin Halving work?
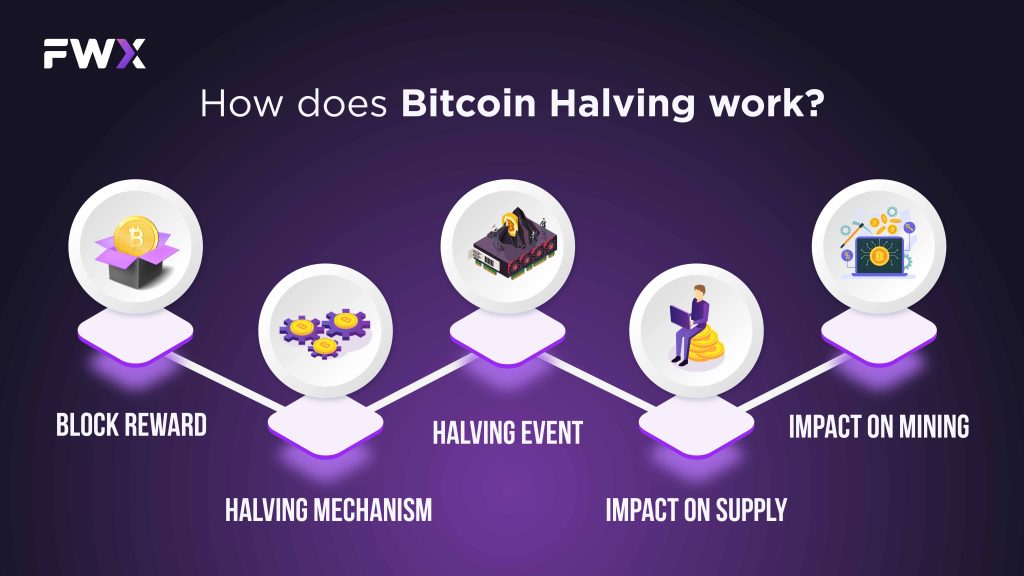
1. Block Reward: The block reward is the amount of Bitcoins awarded to miners for successfully verifying and adding a block of transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain. This reward serves as an incentive for miners to maintain the network and secure the blockchain.
2. Halving Mechanism: The halving mechanism is programmed into the Bitcoin protocol and is designed to reduce the block reward by half every 210,000 blocks. This predetermined schedule ensures a consistent and predictable reduction in the issuance of new Bitcoins.
3. Halving Event: When the 210,000 block milestone is reached, the block reward is automatically reduced by half. This means that miners receive fewer Bitcoins for verifying transactions, effectively slowing down the rate at which new Bitcoins enter circulation.
4. Impact on Supply: Bitcoin halvings play a crucial role in controlling the supply of Bitcoins. By reducing the block reward, halvings slow down the issuance of new coins, mimicking the finite supply of precious metals like gold. This scarcity is believed to contribute to Bitcoin’s long-term value proposition.
5. Impact on Mining: Bitcoin halvings also affect the profitability of mining. As the block reward decreases, miners earn fewer Bitcoins for their efforts. This can lead to increased competition among miners and may prompt some to leave the network. However, the halving mechanism is designed to maintain a balance between miners’ rewards and the overall security of the network.
6. Impact on Price: The impact of Bitcoin halvings on BTC price has been a subject of debate among experts and enthusiasts. While there is no definitive answer, historical data suggests that halvings have often been followed by significant price increases. This is likely due to several factors, including the decreased supply of new Bitcoins, the increased difficulty of mining, and the psychological impact of these anticipated events.
It’s important to note that Bitcoin’s price is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, and halvings are just one piece of the puzzle. Other factors, such as global economic conditions, regulatory developments, and overall market sentiment, can also significantly impact BTC price.
The next Bitcoin halving is expected to occur in April 2024, and it will further reduce the block reward to 3.125 Bitcoins. This event is anticipated to have a significant impact on the Bitcoin ecosystem, potentially influencing mining profitability, supply dynamics, and overall market sentiment.
Bitcoin halving history and dates

Bitcoin halvings have occurred three times since the cryptocurrency’s inception:
| Halving Event | Date | Block Reward Halved From | Block Reward Halved To |
| First Halving | November 28, 2012 | 50 BTC | 25 BTC |
| Second Halving | July 9, 2016 | 25 BTC | 12.5 BTC |
| Third Halving | May 11, 2020 | 12.5 BTC | 6.25 BTC |
| Fourth Halving | April, 2024 | 6.25 | 3.125 |
How Does Bitcoin Halving Effect BTC Price?

The impact of Bitcoin halvings on BTC price is complex and influenced by various factors.
Short-term Impact:
Halving events can lead to increased price volatility in the short term as market participants adjust to the reduced supply.
Anticipation and hype surrounding halvings can trigger buying pressure and price surges.
Long-term Impact:
Halvings contribute to Bitcoin’s scarcity, enhancing its long-term value proposition.
Halvings help maintain the profitability of mining, ensuring network security and stability.
Halvings support Bitcoin’s role as a store of value, similar to precious metals with limited supply.
Investors should exercise caution and conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions.


